B-Splines surfaces#
The B-spline surface in \(\mathbb{R}^d\) associated to knots \((T_u, T_v)\) where \(T_u=(u_i)_{0\leqslant i \leqslant n_u + p_u + 1}\) and \(T_v=(v_i)_{0\leqslant i \leqslant n_v + p_v + 1}\), and control points \((\mathbf{P}_{ij})_{ 0 \leqslant i \leqslant n_u, 0 \leqslant j \leqslant n_v}\) is defined by :
\[
\mathcal{C}(u,v) = \sum_{i=0}^{n_u} \sum_{j=0}^{n_v} N_i^{p_u}(u) N_j^{p_v}(v) \textbf{P}_{i,j}
\]
# needed imports
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib import cm
# importing bsplines utilities
from bsplines_utilities import find_span, all_bsplines, point_on_nurbs_surface, point_on_bspline_surface, insert_knot_bspline_surface, insert_knot_nurbs_surface
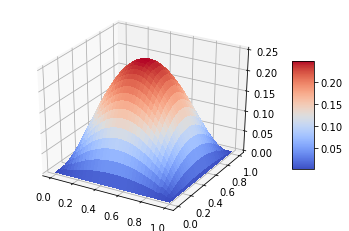
Example 1:
In this first example, we consider a surface that approximate the function \((u,v) \mapsto \sin(\pi u) \sin(\pi v)\)
def example_1():
Tu = [0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 1.]
pu = 2
nu = len(Tu) - pu - 1
Tv = [0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 1.]
pv = 2
nv = len(Tv) - pv - 1
P = np.zeros((nu, nv,1))
gridu = np.linspace(0., 1., nu)
gridv = np.linspace(0., 1., nv)
for i,u in enumerate(gridu):
for j,v in enumerate(gridv):
P[i, j, 0] = np.sin(np.pi*u)*np.sin(np.pi*v)
nx = 101
xs = np.linspace(0., 1., nx)
ny = 101
ys = np.linspace(0., 1., ny)
Q = np.zeros((nx, ny, 1))
for i,x in enumerate(xs):
for j,y in enumerate(ys):
Q[i,j,:] = point_on_bspline_surface(Tu, Tv, P, x, y)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
X, Y = np.meshgrid(xs, ys)
Z = Q[:,:,0]
# Plot the surface.
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap=cm.coolwarm,
linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
# Add a color bar which maps values to colors.
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
example_1()
Example 2:
This example shows the construction of a square in 2D. The B-Spline surface is created using the function make_square
def make_square(origin=(0,0), length=1.):
Tu = [0., 0., 1., 1.]
Tv = [0., 0., 1., 1.]
pu = 1
pv = 1
nu = len(Tu) - pu - 1
nv = len(Tv) - pv - 1
gridu = np.unique(Tu)
gridv = np.unique(Tv)
origin = np.asarray(origin)
P = np.asarray([[[0.,0.],[0.,1.]],[[1.,0.],[1.,1.]]])
for i in range(0, 2):
for j in range(0, 2):
P[i,j,:] = origin + P[i,j,:]*length
return (Tu, Tv), (pu, pv), P
def plot_surface(knots, degrees, P, weights=None, Nu=101, Nv=101, color='b'):
Tu, Tv = knots
pu, pv = degrees
nu = len(Tu) - pu - 1
nv = len(Tv) - pv - 1
gridu = np.unique(Tu)
gridv = np.unique(Tv)
us = np.linspace(0., 1., Nu)
vs = np.linspace(0., 1., Nv)
# ...
Q = np.zeros((Nv, 2))
if weights is None:
for i,u in enumerate(gridu):
for j,v in enumerate(vs):
Q[j,:] = point_on_bspline_surface(Tu, Tv, P, u, v)
plt.plot(Q[:,0], Q[:,1], '-'+color)
else:
for i,u in enumerate(gridu):
for j,v in enumerate(vs):
Q[j,:] = point_on_nurbs_surface(Tu, Tv, P, weights, u, v)
plt.plot(Q[:,0], Q[:,1], '-'+color)
# ...
# ...
Q = np.zeros((Nu, 2))
if weights is None:
for j,v in enumerate(gridv):
for i,u in enumerate(us):
Q[i,:] = point_on_bspline_surface(Tu, Tv, P, u, v)
plt.plot(Q[:,0], Q[:,1], '-'+color)
else:
for j,v in enumerate(gridv):
for i,u in enumerate(us):
Q[i,:] = point_on_nurbs_surface(Tu, Tv, P, weights, u, v)
plt.plot(Q[:,0], Q[:,1], '-'+color)
# ...
# ...
def example_2():
knots, degrees, P = make_square(origin=(0,0),
length=1.)
t = 0.5
Tu, Tv, pu, pv, P = insert_knot_bspline_surface(*knots, *degrees, P, t,
times=1,
axis=None)
plot_surface((Tu, Tv), (pu, pv), P,
weights=None,
Nu=101, Nv=101,
color='b')
example_2()
Example 3:
The following example shows how to create and plots a circle using NURBS.
We shall need the following function:
def make_circle(center=(0.,0.), radius=1.):
Tu = [0., 0., 0., 1, 1., 1.]
Tv = [0., 0., 0., 1, 1., 1.]
pu = 2
pv = 2
nu = len(Tu) - pu - 1
nv = len(Tv) - pv - 1
gridu = np.unique(Tu)
gridv = np.unique(Tv)
s = 1./np.sqrt(2)
P = np.zeros((nu,nv,2))
P[0,0,:] = np.asarray([-s , -s ])
P[1,0,:] = np.asarray([-2*s , 0. ])
P[2,0,:] = np.asarray([-s , s ])
P[0,1,:] = np.asarray([0. , -2*s ])
P[1,1,:] = np.asarray([0. , 0.0 ])
P[2,1,:] = np.asarray([0. , 2*s ])
P[0,2,:] = np.asarray([s , -s ])
P[1,2,:] = np.asarray([2*s , 0. ])
P[2,2,:] = np.asarray([s , s ])
P *= radius
P[:,:,0] += center[0]
P[:,:,1] += center[1]
W = np.zeros((3,3))
W[0,0] = 1.
W[1,0] = s
W[2,0] = 1.
W[0,1] = s
W[1,1] = 1.
W[2,1] = s
W[0,2] = 1.
W[1,2] = s
W[2,2] = 1.
return (Tu, Tv), (pu, pv), P, W
def example_3():
knots, degrees, P, W = make_circle(center=(0.,0.), radius=1.)
t = 0.5
Tu, Tv, pu, pv, P, W = insert_knot_nurbs_surface(*knots, *degrees, P, W, t,
times=1,
axis=None)
plot_surface((Tu, Tv), (pu, pv), P,
weights=W,
Nu=101, Nv=101,
color='b')
example_3()